
Back in the early days of organosilicon chemistry, researchers looked for ways to blend organic functionality with the rugged backbone of silicon. This wasn’t just a pursuit for novelty. They needed stability, heat-resistance, and something that handled moisture better than older materials. Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane, born from these early discoveries, highlighted the growing need for specialty silanes as the plastics, rubber, and electronic industries took off. From my own projects in coatings research, it’s clear how this compound—often referred to by names like Methyldimethoxy(phenyl)silane or Phenylmethylsilicic acid dimethyl ester—helped bridge the gap between laboratory curiosity and a workhorse for surface modification.
Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane falls among compounds prized not for splash but for reliability. The molecule pairs a methyl and a phenyl group onto a silicon atom, finished off with two methoxy groups. It turns up as a clear, low-viscosity liquid with a pretty distinct aromatic smell. Across industrial labs, it comes packed in sealed drums or glass containers, always handled under controlled conditions. From what I've seen, its use underscores just how much detail matters—wrong storage or sloppy transfer, you’ll notice impurities pretty quickly, and sensitive processes don’t leave much room for error.
Transparent and stable under normal storage, it sports a boiling point near 232°C and dissolves in most organic solvents. The molecule resists hydrolysis in dry air but reacts readily when exposed to water, giving off methanol and leading to a silanol derivative—a trait that marks most trialkoxysilanes. I’ve measured its density around 1.02 g/cm³, and you won’t miss the sharp, somewhat sweet odor. Combustion can get troublesome due to the phenyl group; in a fire, expect smoke and irritating fumes. Handling tests in our lab showed modest volatility, so closed systems go a long way to keep vapors down.
Suppliers label bottles with more than a serial number. Every container lists molecular formula (C9H14O2Si), CAS number (3027-21-2), batch purity (typically 98% or better), and recommended storage temperature. Labels usually highlight moisture sensitivity and give basic risk phrases, such as "flammable" and "irritant." I've written out my own batch records for regulatory compliance, and I can vouch that trace metal content, GC purity, and color can make or break material qualification in high-end electronics manufacturing.
Most industry production lines favor alkoxylation of methylphenyl dichlorosilane with methanol, giving dimethoxysilane and methyl chloride as a byproduct. Temperature control and careful exclusion of water become critical—too wet, and you’ll foul your columns. In custom synthesis projects, using thionyl chloride or trimethylchlorosilane streamlines the process. The overall efficiency hinges less on brute yield and more on keeping the product dry and pure, and even small mistakes escalate production costs.
Once you get your hands on methylphenyl dimethoxysilane, the chemistry book opens wide. In my own siloxane synthesis work, I’ve found that the molecule hydrolyzes quickly with water, kicking off condensation reactions that lead neatly to polysiloxane networks. By tinkering with catalysts and moisture, you can control the gelation time or chain structure. During surface modification runs, the dimethoxy groups anchor firmly to glass while the organic arms lend solubility or tune compatibility with other polymers. Methyl and phenyl groups, being stubbornly nonreactive themselves, boost chemical and thermal resistance, which matters greatly for electrical insulation.
On technical datasheets, methylphenyl dimethoxysilane masquerades under names like Dimethoxy(methyl)phenylsilane, Phenyl methyl dimethoxysilane, or even short code tags from in-house catalogs. Keeping up with synonyms makes a huge difference; swapping materials midstream leads to costly mistakes if staff miss subtle nomenclature shifts, especially where regulatory paperwork or import controls keep product names in flux.
You can’t overstate the value of strict adherence to safety guidelines. Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane brings fire hazard and health risks front and center. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) spell out requirements for nitrile gloves, splash goggles, lab coats, and use in ventilated hoods. I’ve seen cases where simple spills turned large workspaces into off-limits zones due to vapor hazards, so keeping spill kits around earns its place. Standard practice also includes weekly checks of storage integrity and signage. In chemical plants, poorly written procedures have led to costly incidents, driving home that training and supervision aren’t bureaucracy—they’re frontline protection. Regulatory benchmarks such as OSHA and GHS inform labeling and risk assessments, forming the baseline for operational protocols.
You notice this silane most in fields aiming to push surface science further. From functional coatings that resist abrasion and weather, to coupling agents in composite materials, methylphenyl dimethoxysilane enables manufacturers to tweak how plastics stick to glass or metals. Electronics producers value it for laying down thin dielectric films, blocking moisture and raising breakdown voltages in circuits. In tire and rubber upgrades, chemical bonding with silica particles translates to higher wear resistance and low rolling resistance. My experience developing moisture-resistant paints taught me to appreciate the molecule’s knack for locking onto surfaces and boosting adhesion, not to mention its role in minimizing porosity.
Innovation teams in material science spend a lot of effort chasing better performance from silicon-based modifiers like methylphenyl dimethoxysilane. In research university labs, chemists keep probing ways to pack more functional groups onto surfaces, aiming for industrial coatings that fend off corrosion or boost electrical insulation. Graduate students routinely use this compound as a foundation in new synthesis schemes, from sol-gel processes to hybrid organic-inorganic materials. Since intellectual property in this space often depends on a unique derivative or novel use, even small tweaks in silane chemistry ripple out through patent filings and product launches. The steady trickle of scientific papers on silane-modified nanomaterials tells a story of constant refinement, propelled by both academic curiosity and practical end-use demands.
Toxicity data for methylphenyl dimethoxysilane aren’t dramatic, yet the risks can’t be brushed aside. Inhalation of vapors irritates airways and eyes, with animal studies highlighting cases of liver and kidney stress at high doses. Regulatory agencies call for airborne exposure limits and recommend routine air monitoring, especially in confined working spaces. Workers who don’t keep up with personal protective equipment have faced rashes and headaches—reminders that skin and mucosal exposure piles up stress on busy operators. I’ve seen safety audits uncover gaps in fume hood integrity or spill mitigation, leading to targeted retraining and investment in better engineering controls.
Growth in advanced electronics, automotive composites, and energy storage materials keeps demand climbing for higher-performing silanes. Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane won’t fade from view as manufacturers hunt for cost-effective methods to make devices thinner, lighter, and more resistant to tough environments. Trends point toward greener alternatives and process improvements that cut hazardous byproducts, both to keep ahead of regulations and to reduce the headache of waste management. If past decades of organosilicon chemistry offer any lesson, it’s that practical problems drive the next generation of advances, and every new application builds on insight earned from old synthesis flasks and hard-fought production runs.
Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane doesn’t get much airtime outside chemistry circles, but its impact hides inside products most of us touch every day. The secret is in its structure—two methoxy groups and a mix of methyl and phenyl rings bonded to silicon—giving chemists real flexibility. I remember first coming across the compound years back in a surface-coatings course, reading case studies about how its small tweaks could change a whole paint’s water resistance. It became clear pretty quickly that these molecules have more to offer than the lab jargon suggests.
Industries rely on coatings to make surfaces last longer or fight off rust, sunlight, or oil. Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane slides in as a building block for these protective layers, especially in paints, varnishes, and adhesives made with siloxane chemistry. Add a bit to a resin mix and that product will resist wear better or shrug off water a little longer. I’ve seen consumer goods like watch faces and smartphone components last years tougher when these specialty chemicals get baked into their outer shells.
Silicon materials play a huge role in electronics. The phenyl group brings extra stability against heat. That’s why circuit boards and cables often get a protective layer spun from silane compounds used as primers or crosslinkers. Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane steps up by improving the bond between plastic and glass, or between rubber and metal. Lots of devices rely on that invisible connection to keep things from cracking or short-circuiting—especially when things heat up. Having worked in electronics recycling, I've had my fair share of experience seeing how better surface treatments mean less waste because the gadgets don’t fall apart as soon.
You might not notice, but the same silicon magic plays a role in stains and streaks left behind by rain or hard water. Glassmakers and ceramic manufacturers treat surfaces with silane-based agents to help repel water, mud, and oil. This makes windshields, tiles, and mirrors easier to keep clean, which saves time and limits aggressive chemical cleaners. That makes a difference at home and in businesses, cutting maintenance costs and environmental damage from harsh washing agents.
One big concern is how workers and end users stay safe. Some silanes produce methanol as a byproduct, which requires careful handling. Companies set up air monitoring and good ventilation in factories. I’ve worked at a plant where training on chemical handling wasn’t just a one-time thing, but a regular drill. Long-term, more research looks at alternatives—compounds with lower toxicity—so that personal protective equipment can play a smaller role without putting anyone at risk.
The silane market responds to calls for eco-friendly and sustainable solutions. As regulatory agencies ask for safer ingredients, the pressure is on to revisit old formulas and find ways to use less, or to invent similar molecules from renewable materials. We’ve already seen hybrid coatings with a fraction of the usual solvent load, which means better air quality. There’s potential in open collaboration between manufacturers, universities, and public health experts to draft chemicals that offer the same durability with a softer impact both on workers and the planet.
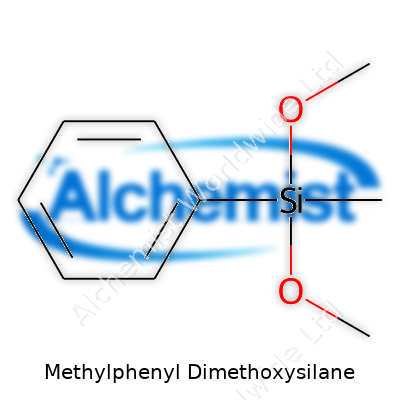
Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane looks like a mouthful, but it boils down to silicon chemistry and real applications. Its chemical formula, C9H14O2Si, packs a punch in the world of materials science. This means you’ve got a molecule with nine carbon atoms, fourteen hydrogen atoms, two oxygens, and one silicon. These numbers aren’t picked from thin air. Each part comes together with intention, giving the compound structure and properties that help industries do more than sit on their hands.
My own experience in the lab taught me early on: knowing a chemical’s formula is a ticket to understanding how it behaves. Picture methylphenyl dimethoxysilane: the methyl group brings a touch of hydrophobicity, phenyl sneaks in stability, and dimethoxy means two methoxy groups hanging off silicon. This makes the molecule ideal for modifying surfaces, especially in the making of silicone rubber, resins, or specialty glass.
People often see these applications as distant, yet if you’ve ever walked on a glossy floor or used a waterproof phone case, you’ve touched materials shaped by silane chemistry. Industry workers use this compound for functional coatings, adhesives, and advanced polymers that keep things together under heat and stress.
Scientific trust builds on transparency. The chemical identifiers for methylphenyl dimethoxysilane back up the facts: the formula checks out with databases like PubChem and ChemSpider. This isn’t trivial paperwork, either. Safety data reveals you don’t mess around with this stuff in a home kitchen. Mishandling can lead to irritation or worse, so anyone working with it ought to lean on proper gear, training, and ventilation. I’ve found that respect for the material always wins over casual shortcuts.
Knowing the structure helps manufacturers shave costs, control performance, and boost sustainability. The two methoxy groups make the compound ready to react, giving engineers ways to fine-tune products for everything from automotive trim to solar panels. Yet, this same reactivity can spill into the environment if waste processes stumble.
I remember a case in a local plant where improper handling of a silane blend led to air quality headaches. Those experiences remind us: beyond numbers on paper, real-world consequences ride on how we steward chemicals from lab bench to disposal. The formula isn’t just for textbooks—it’s a map for managing risk and advancing tech responsibly.
Solutions never rest on knowing the numbers alone. Training matters—people handling chemicals like methylphenyl dimethoxysilane benefit from up-to-date safety protocols, regular checks on storage, and clear emergency steps. Companies investing in less hazardous alternatives or improved containment have seen fewer accidents and fewer headaches. Taking time to teach material science basics to staff, not just supervisors, bridges the gap between safety manuals and real action.
Having the formula, C9H14O2Si, does more than fill a data sheet. It shapes how we design our products, safeguard health, and imagine next-generation materials. That’s experience talking—science grounded in the details, tested in the day-to-day of industry and research.
Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane pops up in a lot of industrial work. People use it to make silicone resins, coatings, and sealants. It helps create a water-repellent layer on glass and metal, and finds its way into the electronics business and other manufacturing spaces. Its chemical structure—a mix of silicon, methyl, and phenyl groups—lets it bond well with lots of surfaces, so it’s pretty versatile in labs and factories. But versatility doesn’t mean safety, and that’s where things get interesting.
Most of us don’t come across methylphenyl dimethoxysilane in daily life, but the folks working with it in factories or research labs face direct exposure. Breathing in its vapors can irritate your nose, throat, and lungs. Skin contact can bring on dryness, redness, or even burns—especially if nobody wears gloves. Direct eye exposure always spells trouble with any silane, and this one’s no exception. The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for methylphenyl dimethoxysilane spells it out: it can cause pain, serious irritation, and potential long-term harm if someone gets splashed. Inhaling a lot of silane vapor at once may lead to dizziness or headaches, though there’s no strong link to chronic toxicity in humans when used as intended. Still, toxic effects add up with enough repeated contact.
This chemical brings fire risks on top of health problems. Once it hits water or air, it breaks down to chemicals like methanol, which can be flammable and toxic. Storage always calls for proper containment, reliable labeling, and clean-up routines. If spilled, it can spread into drains, and trace amounts may burden wastewater treatment. Harm to aquatic life isn’t fully mapped out, but other silanes show that even a small release can do damage if it migrates into rivers or lakes.
Many industries try to swap out harsh chemicals, but methylphenyl dimethoxysilane still wins out where that distinctive silicon bond is needed. I’ve seen people working with silanes who didn’t know about the risks and missed simple safety steps—skipping gloves or working in cramped, poorly ventilated rooms. Problems multiply fast if supervisors skip regular safety training. Factories keep things safer by using local exhaust vents, handing out chemical-rated gloves, and making emergency showers handy. Having a solid set of best practices, refreshed every year, goes a long way. Telling workers why they’re doing something, not just what to do, leads to fewer shortcuts.
People in charge should set up clear ways to monitor exposure. It matters to check the air in the workspace and to get a clear schedule for skin checks, especially for folks using large quantities. Spill plans, fire extinguishers, and regular walk-throughs help spot problems before they turn major. Basic things like proper labeling or tightly sealed containers help cut down on accidents. Responsible disposal matters, too—pouring old silane down the drain isn’t just bad practice, it invites hefty fines and environmental headaches.
Experts, authorities, and plant managers do best sharing data on accidents and illnesses. Real-world info beats theory every time. Industry groups and government agencies owe it to workers to update guidelines when new evidence emerges. Open discussion lets people see red flags sooner, and avoids hidden dangers down the line. Everyone in the supply chain—company staff, regulators, cleanup crews—deserves honest facts. Methylphenyl dimethoxysilane plays a big role in modern manufacturing, and a little extra care keeps progress from coming at the cost of people’s health or local ecosystems.
Most chemical accidents begin with small oversights. Shelving a volatile compound near a heat source or in a humid corner might seem harmless, but the risks add up. I’ve learned in every lab job that storing chemicals isn’t just about following rules. It’s about respecting the substance in front of you. Methylphenyl Dimethoxysilane, like plenty of silane compounds, responds badly to carelessness. You don’t need a disaster story to appreciate why storage takes center stage.
I always check the thermometer and hygrometer before restocking shelves. For this chemical, a cool setting below 25°C limits vapor buildup. High temperature encourages decomposition and can pop open containers. Humidity brings another headache, as water vapor can trigger unwanted hydrolysis, releasing messy and dangerous byproducts. Storing this compound in an air-conditioned storeroom, away from direct sunlight or steam lines, makes spills and fumes less likely. I remember a warehouse that skimped on temperature control; one summer day left the safety officers working overtime to manage swelling drums and ruined product.
I like to picture every container as a sentry post. Any slack with caps, seals, or closures lets moisture sneak in. Once opened, airtight resealing beats any other precaution. Glass or metal suits these needs better than porous plastic, which can leach fumes or warp if the clear guidelines aren’t followed. Every label has to stay sharp and easy to read, with hazard diamonds and emergency contacts in bold. Clear labeling helped an old colleague of mine catch a mix-up before a shipment left the dock, stopping what could have been a hazardous delivery error.
An orderly shelf helps avoid cross-contamination. In shared spaces, it’s easy to place containers too close to acids, oxidizers, or water-based chemicals, risking violent reactions. Assigning a dedicated zone for silane compounds, reinforced by spill containment trays, pays off in peace of mind. I always check secondary containment for leaks, because a simple crack in a tray could mean hours of cleaning and expensive waste disposal.
Poor airflow lets vapors accumulate. In one startup, the makeshift storeroom had no functional exhaust; the faint sweet smell after a few days clued everyone in to the buildup. Part of proper storage ties back to having fume extraction and air monitoring. That keeps not only the chemical stable but everyone else comfortable working nearby.
Every delivery brings a new batch, and sometimes differing container specs. Sourcing from certified suppliers with documented protocols always gives more consistent results. I’ve found monthly audits with a fresh checklist help spot dated inventory or failing containers before serious risk emerges. Record-keeping doesn’t feel glamorous, but one missed log entry can wildfire into insurance claims or workplace injury reports.
Training is as critical as any shelf or air duct. New staff get a walk-through of handling procedures, spill response, and the exact steps for storage. My first mishap came from not knowing which absorbent pad worked with silanes. With methylphenyl dimethoxysilane, using the wrong cleanup can escalate a small spill. Stocking the right PPE and cleanup tools nearby turns a nervous situation into a routine fix. These habits build trust and reduce turnover among warehouse and lab workers alike.
The storage of methylphenyl dimethoxysilane asks for diligence, not paranoia. Clear habits—from airtight storage and robust labeling to regular temperature checks and emergency training—keep facilities safer. Every small step towards better storage stitches a stronger safety net for the entire operation.
Anyone working in chemical manufacturing or surface treatment labs will know that even a small bottle of Methylphenyl Dimethoxysilane packs plenty of risk along with its benefits. Every step from receiving a shipment to waste collection calls for common sense and some serious care. The liquid brings value to coatings and polymers, but it does so with hazards that can’t be ignored. A slip-up here doesn’t just cost a few dollars—it endangers health and safety.
Lab coats, gloves, and tight-fitting goggles aren’t fashion accessories. Skin contact with this stuff leads to real problems—irritation, redness, and sometimes worse effects. Inhaling vapors, even during a quick transfer between containers, can cause headaches, dizziness, or more pronounced respiratory problems. Anyone who’s spent time handling silanes will tell you: grab a respirator where ventilation falls short. Keep spill kits within arm’s reach and never leave unmarked containers lying around.
Most chemical users have seen the aftermath of spills left to dry on bench tops. These mark not just laziness but a hazard waiting to escalate. The trick here is to set a routine: clean as you go, double-check seals, and keep walkways clear. Even short exposure times build up over months and years. The facts back this up—repeated incidents stretch both health resources and company budgets thin.
Most scents from silane vapors drift through labs faster than you notice, and with enough spilled liquid, drains appear tempting. That path shoots problems downstream. Methylphenyl Dimethoxysilane breaks down slowly and can harm aquatic life. Rushing disposal leaves lab techs and building management facing fines and reputational damage. Stashing solid waste in proper containers, making sure they’re labeled for hazardous pickup, turns caution into habit. I’ve seen teams do it right and watched their labs stay out of the compliance officer’s spotlight. If only every group handled waste that methodically.
You don’t need to lock this chemical behind vault doors, though storing it near a heat source or in the sunlight shortens its lifespan and raises risk. Keep bottles dry and cool, separated from acids, strong oxidizers, and moisture. Silanes react when they meet water, and the fumes will remind anyone in the room of that mistake. Keep inventory updates current. In my own work, running a quarterly check saves drama: no outdated chemicals, no mystery stains, fewer headaches during audits.
Even trained teams get caught by surprise—what matters is how people respond. Written procedures, fire extinguishers close by, eyewash stations ready to use: these form the backbone of good practice. Drills shouldn’t feel like empty rituals. Each one preps people to tackle a real spill, not just read about it in a binder. Hospitals report that quick, thoughtful action cuts injuries short and puts everyone on safer ground.
Taking shortcuts tempts fate, and it’s not just newcomers who fall into the trap. Every chemical has its quirks, and Methylphenyl Dimethoxysilane brings enough of them. Stick to up-to-date guidelines from the manufacturer and agencies like OSHA. Regular reviews build confidence. If you ever feel uncertain, ask someone with more experience. In labs I’ve worked in, the best prevention starts with curiosity and sharing knowledge up and down the team.
Building habits around precaution doesn’t take heroic effort; it relies on small, steady steps and clear communication. Frequent reminders, open reporting of near-misses, fast fixes for storage or disposal errors—these shape a culture people can trust. In practice, well-handled silanes mean more than compliance. They ensure everyone gets home healthy, every day.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | [methoxy-(methyl)-phenylsilane] |
| Other names |
Dimethoxy(methyl)phenylsilane Methyldimethoxyphenylsilane Phenylmethylsilane, dimethoxy- Dimethoxyphenylmethylsilane |
| Pronunciation | /ˈmɛθ.ɪlˌfiː.nɪl daɪˌmɛθ.ɒk.siˈsaɪ.leɪn/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 3027-21-2 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1362201 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:87357 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2110864 |
| ChemSpider | 21566195 |
| DrugBank | DB14408 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 07c07b39-6cb5-4a3b-ada2-5282d13bb2d9 |
| EC Number | 203-624-3 |
| Gmelin Reference | 83494 |
| KEGG | C19268 |
| MeSH | C10H16O2Si |
| PubChem CID | 66290 |
| RTECS number | VV9275000 |
| UNII | 1VK6F3E4SB |
| UN number | UN1993 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID6058586 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C9H14O2Si |
| Molar mass | 180.29 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless transparent liquid |
| Odor | Aromatic |
| Density | 0.993 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| log P | 1.8 |
| Vapor pressure | 1 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | Acidity (pKa): 35.1 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -68.0×10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.468 |
| Viscosity | 1.5 mPa·s (25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 3.15 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 350.95 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -318.3 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -6811.6 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS02,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+P310, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0 |
| Flash point | 88 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 270°C |
| Explosive limits | Lower: 0.9% Upper: 8.6% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (oral, rat): 3600 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral rat LD50: 2407 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | GV9175000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL (Permissible Exposure Limit) for Methylphenyl Dimethoxysilane: Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 10 ppm |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Not established |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Phenyltrimethoxysilane Methyltrimethoxysilane Dimethyldimethoxysilane Diphenyldimethoxysilane Methylphenyldiethoxysilane |