
Silicone chemistry started to surge after the Second World War, but the world didn’t really meet most modern organosilanes, like vinylmethyldimethoxysilane, until the 1950s. The demand for stronger, more versatile adhesive solutions drove research; the old construction world just couldn’t get enough of reliable, long-lasting bonds. Chemists realized that silane coupling agents, with their dual reactivity toward both organic molecules and minerals, could solve problems that neither old-school glues nor simple resin blends could touch. By the late 20th century, vinyl-functional silanes started flowing out of European plants. From what I’ve seen in R&D files, American, German, and Japanese researchers all worked to refine the molecule's structure, pushing for more stability, better storage, and higher purity. Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane ended up in plenty of high-value applications because it wasn’t picky about reacting with the surfaces of silica or with different resin groups. Its adoption snowballed as the electronics, automotive, and construction industries realized silanes could literally change the game for adhesives, paints, and composites.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane isn’t a commodity chemical, but anyone dealing with advanced coatings, sealants, or plastic compounding will brush shoulders with it sooner or later. Its molecule features a vinyl group—think of that as a hook for organic chemistry—and two methoxy groups on the silane, which readily open up for hydrolysis. The methyl decoration gives it enough hydrophobic character to survive storage and handling without rapid hydrolysis, making shelf stability a big plus. Most suppliers offer it as a clear, colorless liquid, giving it an approachable look for laboratory and plant technicians alike. Its chemical packaging often provides UN numbers for safe handling, and technical data sheets aren’t shy about specifying exactly how much water can trigger its reactivity.
The stuff pours thin, about as runny as acetone. It boils around 105°C to 108°C at normal pressure, so extra ventilation in the lab becomes a must. A sharp, ether-like odor prickles the nose, telling experienced hands to work with a little caution. Density clocks in around 0.95 g/cm³, and refractive index sits near 1.39. What stands out most is its hydrolytic reactivity: let a whiff of moisture in, and those methoxy groups break into alcohol and silanol groups, which grab onto glass, minerals, or metal surfaces at a molecular level. People who work with silanes sometimes forget: hydrolysis isn’t just a technical detail, it's what brings the molecule to life as a coupling agent or surface modifier. Incompatibilities arise with strong acids, bases, or water, so any leaks or spills quickly demand attention.
Specification sheets for vinylmethyldimethoxysilane run dense, but common details include an assay of at least 98% by GC, water content below 0.1%, and color less than 20 APHA. Package labels carry GHS hazard diamonds, signal words like “Danger," and H phrases warning of flammability and vapor irritation. You’ll see UN1993 on every drum shipped internationally, with additional EU and DOT identifiers. Some manufacturers add batch traceability codes and shelf life, typically eighteen months under dry nitrogen or argon. Labels require a lot of reading to get it right, but with something this reactive, skipping steps creates headaches for logistics teams—especially with customs and workplace regulators checking compliance.
Industrial routes usually start with chloromethylvinylsilane, reacted with excess methanol in the presence of an acid scavenger. The reaction cranks out HCl gas, so closed reactors suck up the byproducts while ensuring the product doesn’t see a drop of water before packaging. Small labs tempted to scale up quickly run into trouble with moisture, since even the air’s humidity can kill a batch’s performance downstream. Removing residual acids and unreacted alcohol calls for careful distillation. Production teams rely on stainless steel or glass-lined vessels to avoid metal catalysis; nobody wants to scrap a 100-kilogram batch due to black crud at the bottom of the tank.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane lives for reaction. The double-bonded vinyl group crosslinks into everything from polyolefins to acrylics. Meanwhile, those methoxy groups hydrolyze on demand, breaking off as methanol and letting the silicon anchor itself to a mineral surface or a functionalized resin. Silane chemistry can look deceptively simple on paper, but getting a reproducible bond both on the organic and inorganic sides needs real finesse. This molecule’s ability to co-polymerize means it shows up as a modifier in hot-melt adhesives and composites. Those who work in resin formulation spend hours dialing in dosing rates—too much, and the final composite becomes brittle; too little, and no improvement shows at all. Modifying this molecule with longer alkyl chains or adding a second functional group keeps pushing its uses into new areas, with researchers always chasing stronger, more weather-resistant bonds.
Over the years, this molecule picked up quite a few aliases. Some catalogs list it as vinyl(methyl)dimethoxysilane or VMMS. Dow’s Silquest A-2171 and other supplier brands tout proprietary blends, sometimes tweaking isomer content or stabilizer mix. International trade logs mark it as CAS 16881-77-9. Generic naming conventions don’t simplify things for buyers, who often sort through a dozen similar-sounding silanes. Synonym confusion fills discussion boards and industry meetings, especially since improper substitution in a blending operation can send an entire production run to waste.
Experience teaches respect for chemicals that can flash off, sting the lungs, and foul process lines. At low concentrations, vinylmethyldimethoxysilane vapors irritate eyes and nasal passages; contractors who ignore personal protective equipment learn quick lessons. Handling guidelines call for working under local exhaust ventilation, with gloves, goggles, and long sleeves as the gold standard. Facilities rely on flame-resistant cabinets, since the liquid can ignite at 18°C. Most spill kits include clay absorbents and sealing containers for cleanup, and SOPs drill teams on keeping water away from inventory storage. Air monitoring for methanol vapor proves wise in plant environments, especially during bulk transfers or drum openings. Companies investing in engineering controls cut risk and keep the stuff from becoming a safety headline.
Polymer compounding labs view vinylmethyldimethoxysilane as an answer to poor filler dispersion and weak interfacial bonds. In cable sheathing or plastic piping, it acts as a coupling agent, letting simple polyethylenes accept mineral fillers without turning into crumbly messes. Adhesives engineers prize the molecule for boosting strength and environmental resistance, especially in challenging spots like car assemblies or wind turbine blades. Many construction sealants owe their elasticity to silane crosslinking, which keeps them watertight season after season. During my own read of patent literature, I’ve noticed its presence in moisture-cure polyurethane systems, where only precise dosing achieves both flexibility and bond longevity. Electronics packaging relies on this silane’s ability to prime glass and ceramics, supporting die-attachment and encapsulation in demanding thermal cycles. Each industry tweaks application doses and methods to squeeze out performance while controlling costs.
Industrial R&D crews continue finding new tricks for this silane. Current work centers on using vinylmethyldimethoxysilane to upcycle commodity plastics, making everything from recycled polyethylene stronger and longer-lasting. Universities and collaborative research clusters are exploring its use in nanocomposites, where every molecule counts for electrical or barrier properties. Surface science teams probe the exact mechanisms of silane grafting, chasing after models that predict and control hydrolysis in complex real-world environments. The challenge always lies in balancing reactivity—react too soon, and product handles poorly; react too late, and bonds never form. This delicate dance shows up again and again in research journals, with digital twin modeling and high-throughput synthesis now cutting bench times that used to stretch for months.
Toxicologists keep a wary eye on vinylmethyldimethoxysilane. Inhalation brings acute irritation; animal studies show reversible membrane effects at lower doses but call for more work on chronic exposure impacts. Methanol, formed from hydrolysis, presents well-known risks including headaches, nausea, and in severe cases, nerve damage; plant workers now recognize early symptoms and turn to medical protocols quickly. Long-term environmental fate gets a close look. Researchers explore how runoff in water treatment or soil systems leads to possible degradation byproducts. So far, regulatory agencies in the US, EU, and parts of Asia set occupational exposure limits and wastewater discharge rules. That regulatory landscape keeps shifting as more real-world epidemiology and environmental health studies come out, and industry safety teams don’t have the luxury of ignoring emerging guidance.
Product development teams and industry analysts both expect demand to climb with the growth of lightweight composites, electric vehicles, and miniaturized electronics. Research into more sustainable and less toxic alternatives moves forward, but so far, traditional organosilanes keep their edge with sheer performance and availability. Artificial intelligence and machine learning now help chemists predict new silane structures with even greater performance or environmental stability. Circular economy trends push for better recycling and upcycling of silane-modified plastics. Investing in green chemistry routes that reduce waste and energy, while integrating with existing manufacturing, looks like the next big test. The pressure also builds for safer-by-design molecules that cut occupational exposure while keeping the reliability of legacy silanes. At every stage from lab bench to plant floor and end-of-life disposal, continuous improvement remains crucial for the future of vinylmethyldimethoxysilane in a more responsible and resilient industrial landscape.
If you flip over a smartphone case, poke at a kitchen sealant, or run your hand along a glossy window frame, chances are you’ve brushed up against a bit of vinylmethyldimethoxysilane. That mouthful of a chemical brings together silicon and organic chemistry in a way that quietly keeps countless products tougher, more flexible, and water-resistant. I used to think of vinylmethyldimethoxysilane as some niche lab material, but it turns out it’s one of those behind-the-scenes ingredients that keeps the world glued together—literally.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane makes a direct impact wherever strong bonds are needed between what usually wouldn’t stick—organic stuff and inorganic surfaces. With a vinyl group on one end and methoxy groups on the other, it grabs on to both plastics and glass, rubber and metal, and even concrete. Think of it like a two-way handshake at the molecular level. Manufacturers rely on it as a coupling agent and adhesion promoter, so two vastly different materials act more like a team than strangers forced to sit next to each other.
I’ve spent years working with folks in construction and electronics, and I see this chemical in action everywhere. In the world of cables, vinylmethyldimethoxysilane gets added to crosslinked polyethylene insulation. Without it, power lines might turn brittle, wires could lose their protective jackets, and weather exposure would chew through material faster. I remember seeing old power cords dry and crack in the sun, long before silane technology caught on. Now, cables last years longer and deal better with rain and heat.
Sealants and adhesives also owe a debt to this silane. By improving the bond strength between surfaces, doors and windows seal tight, floors stay waterproof even after years of traffic, and glass doesn’t pop loose the minute a frame flexes. Automotive makers use it in weatherstripping, helping keep cars quieter inside and holding their shape through endless heat cycles. Those little changes in durability add up, saving energy and trimming down repair bills.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane stands out for its flexibility, but it’s not without headaches. It hydrolyzes in moist air, so storage needs to stay bone dry and bottles tightly sealed. Accidental contact means itchy skin or watery eyes, which reminds me of the times I’ve had to wrangle a leaky drum in a warehouse. Responsible handling isn’t just about rules—good ventilation and protective gloves keep workers healthy and focused.
Some factories look for ways to reuse waste from silane production, or seek alternatives with less environmental baggage. Biodegradable agents are coming along, but reliable, affordable options still lag behind. The industry keeps making strides, driven by tighter regulations and a push from consumers demanding greener products. Engineers and chemists will need to keep asking tough questions about where raw chemical advantages really pay off, and where a gentler touch could fill in.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane probably won’t ever become a household name, but its mark on everyday life runs deep. Better adhesives, smarter building materials, durable everyday tools—these benefits show up without fanfare. Staying curious about how and why these chemicals get used leaves us ready for the next wave of smarter, safer ideas that put both people and the planet first.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane plays a key role in manufacturing and chemistry labs—especially across plastics, adhesives, and electronics. Coming from someone who's watched friends in industry rush a job and pay the price, it’s not a chemical you should underestimate. The liquid itself gives off fumes quick, and skin contact or even splashes become dangerous faster than many realize. Inhaling those vapors brings headaches, throat irritation, and sometimes worse if exposure runs long. Skin reacts with redness or burns, while eyes get irritated and stung. So, even a small spill in a busy lab can turn an easy day into a hard lesson in minutes.
Plenty of safety data sheets pile up in labs, but nothing replaces real experience. Every worker handling this stuff must use chemical-resistant gloves—nitrile or butyl rubber, not the thin latex you grab for janitorial cleaning. Goggles keep those microscopic splashes from becoming an emergency room story, and face shields help when working with volumes above a few milliliters. A long-sleeved, chemical-resistant lab coat and shoes that cover the top of your foot close the gaps. Don’t skip the fit test on respirators if vapors start showing up. Even in a well-ventilated place, a spill or thermal reaction can choke up the air faster than expected.
A lab without good ventilation feels like bad news: the smell, the heaviness in your chest. Any technician running reactions with this silane needs more than a cracked window. Fume hoods protect against direct vapor exposure, and using local exhaust systems reduces lingering concentrations indoors. Most folks remember to switch on the fans, but checking that those fans actually pull air before work starts can save a lot of grief. I’ve seen colleagues step back from the edge before a reaction simply because a hood alarm failed—tests with a chemical smoke stick make a big difference.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane reacts with water to make methanol and other byproducts that nobody wants to breathe. Keep this chemical dry and tightly sealed. Storing in a cool, well-marked flammable cabinet with the right signage avoids mix-ups. I’ve witnessed more than one panic because someone stored incompatible chemicals side-by-side—always double-check labels. A small leak? Don’t mop with water. Absorb with sand or something silica-based, place used materials in a sealed bag, and move them away from people as soon as possible.
People sometimes tune out reminders. After years alongside experienced operators, one thing remains true: thorough, routine training prevents emergencies. Workers recognize symptoms of exposure, read the labels, and don’t cut corners with PPE or cleaning. Emergency procedures posted in plain sight beat a buried safety manual every time. Quick access to eyewash stations, showers, and clear labels create layers of protection. Anyone who touched this chemical without knowing exactly what to do next has ended up regretting it.
Teams that share knowledge and pay attention to the little things avoid major accidents and downtime. Companies with the best track records check in on each other and speak up before bad habits set in. In my own experience, respect for hazardous chemicals grows from stories, mistakes shared, and building routines together. Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane doesn’t forgive carelessness—informed action and real caution keep everyone going home healthy at the end of the shift.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane stands out in the silicone world for its unique molecular setup. This compound carries the formula C5H12O2Si. Looking closer, its structure brings together one vinyl group (-CH=CH2), a methyl group (-CH3), and two methoxy groups (-OCH3) all attached to a single silicon atom. Chemists write it as CH2=CHSi(CH3)(OCH3)2. The silicon center acts as the anchor, and each of its bonds shapes the chemical’s properties, giving us a tool that connects different types of materials.
The versatility of vinylmethyldimethoxysilane circles back to its structure. Industrial labs use this molecule to connect organic and inorganic systems – think about bonding plastics to glass, or letting new rubber materials stick better during processing. The vinyl group helps with cross-linking, letting the material form strong, lasting bonds, especially in harsh environments. Two methoxy groups make the molecule reactive in moisture, allowing it to create a tight bond with substrates, whether that’s glass, ceramics, or even metal surfaces. These combinations help industries make coatings, sealants, and adhesives that last.
All chemicals require attention to safety, and this one is no exception. Direct exposure may irritate the skin or eyes, and overexposure by inhalation can bother the respiratory tract. From personal experience working in a materials lab, eye protection and gloves become non-negotiable. Proper handling, with good ventilation, protects workers and keeps production lines running efficiently. Following recommendations from trusted sources—like workplace safety sheets and regulatory boards—supports smart decision-making throughout the process.
It’s easy to overlook the broader changes that vinylmethyldimethoxysilane brings to manufacturing. Products that last longer mean less waste and a slower rate of replacement. In construction, better bonding translates into weather-resistant windows and doors. In electronics, its structure helps make moisture-resistant coatings—something that keeps devices working after a spill or sudden storm. These advances might seem small, but over time, they shape how resources get used and how safe finished products remain for families and workers.
Moving ahead, it helps to invest more in alternatives that minimize risks and keep the same strong bonds. Training staff well and keeping them informed strengthens workplace safety. Fast action on spills, clear labeling, and regular safety reviews prevent minor problems from becoming major incidents. Manufacturers can support recycling programs by designing silanes that break down more easily after a product’s life ends, cutting down on chemical leftovers in landfills. Efforts to improve transparency and compliance with regulations, especially those laid out by international safety organizations, raise the bar for quality. This creates better trust with customers and keeps products safe as they move around the world.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane connects raw science with everyday solutions. Scientific know-how, responsible use, and updated safety practices let everyone play a part in using chemicals wisely. Commitment to chemistry and safety helps both industries and communities move forward with confidence.
Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane doesn’t give off warning signs like a leaking drum, but beneath the surface, it calls for respect in handling. This chemical turns up in places like adhesives, sealants, and coatings—areas where many of us earn our living. Keeping it safe not only protects investments but also keeps people and the environment out of harm’s way. Mistakes have cost real lives and livelihoods before, so care isn’t just a suggestion—it’s a responsibility.
Chemicals like this don’t take kindly to moisture. Even a little bit of humidity can set off unwanted reactions, forming methanol along the way—a flammable, toxic substance nobody wants hanging around in the air. I learned early on in my lab days: just a crack in a seal could cause a headache for a whole crew. This is why putting it in a tightly sealed container, usually glass or high-quality plastic, means less chance of an accident or spoiled materials. Skipping on that step risks wasted product and hazardous clean-ups.
Temperature swings cause more than just product clumping or leaks. Chemical stability drops off if things get too warm or too cold. Store these containers somewhere cool. Most facilities keep this sort of chemical at room temperature, aiming for around 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), and away from heating pipes or hot summer sun. It’s tempting to stash containers in easy-to-reach places, but a climate-controlled storeroom cuts emergencies down to size.
No one talks enough about what happens if flammable stuff isn't separated from ignition sources. Forklift sparks, extension cords, or even a carelessly flicked cigarette can trigger disaster. Shelves built from metal or sturdy plastic keep containers steady and away from windows, floor drains, or direct light. Busy areas create more chances for mistakes, so setting aside a clear, locked section just for chemicals works best.
Legible, complete labels on every container—these make life easier when auditing materials or transferring product. I once saw a mix-up where two clear liquids shared the same unmarked jug. It cost three days of sorting and hours on the phone with hazardous waste removal contractors. Keep original labels intact and never decant leftover product into mismatched bottles. If the wrong person grabs the wrong container, the costs multiply fast.
Having clear signage and good ventilation helps lower risk even more. Airflow prevents any accidental releases from concentrating, dropping the odds of someone breathing in fumes or a stray spark causing trouble. Staff training should run regularly, covering emergency procedures and chemical properties. Knowing how to clean up drips, neutralize spills, and use a fire extinguisher pays off tenfold compared to simple reminders tacked on noticeboards.
Expired or degraded chemicals become harder to handle and sometimes react in unexpected ways. I’ve seen neglected stock turn from a valuable resource into a disposal nightmare. Rotate stock like grocery stores do: first in, first out. Documenting batch numbers and purchase dates makes tracking easy, and it stops old containers from gathering dust at the back of the storeroom. Regular walkthroughs, combined with solid record-keeping, means surprises stay rare.
Protecting people and property never comes from luck. It grows out of careful habits, good systems, and a willingness to take storage seriously—every single time.Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane brings impressive benefits to the world of plastics and rubber manufacturing. For plastic cable insulation, its chemistry helps form strong chemical bonds between inorganic fillers and organic polymers. Cables and wires keep their mechanical strength and resist heat and moisture, because the bond doesn’t let water or dust break it down. In automotive and appliance parts, shock resistance’s not just a buzzword—it keeps products from snapping and cracking over time. Companies also rely on this silane in the formulation of shoe soles, hoses, and weatherstripping, each item benefiting from toughened flexibility and a longer usable life.
Few products would last without adhesives or sealants that don’t degrade after exposure to rain, sun, or household chemicals. Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane acts like a matchmaker between tough substrates—such as glass, metal, or ceramics—and synthetic adhesives. I’ve seen window assemblies fail because the sealant separated during winter storms; with this silane in the mix, the bond holds against seasonal expansion and contraction. Construction teams turn to it for caulks that refuse to peel or crack around windows, baths, and countertops. The chemistry behind it stops failure where air and water threaten to sneak in.
Protective coatings show their worth on bridges, industrial equipment, and even bicycles. Here, vinylmethyldimethoxysilane helps build resistance to corrosion and fading. Once, I toured an old warehouse before a renovation and saw faded paint flaking from every pipe—products treated with functional silanes last far longer, cutting down on both safety risks and repair costs. Paint formulators add it to help the pigments stick to metal, glass, or concrete. Manufacturers save money, waste less, and end up extending the life of everything from marine vessels to outdoor playgrounds.
Miniaturized electronics can’t survive dampness or heat without proper protection. In printed circuit boards and encapsulants, this silane keeps moisture out of sensitive electronics. Reliable connections prevent malfunctions and cut down warranty returns—I’ve heard engineers say the right silane is the difference between a device working for months instead of years. Once it’s mixed with epoxies or silicone gels, even the small hairline gaps become sealed, so consumer electronics stay durable in pockets, kitchens, and workshops.
Some people worry about workplace exposure or environmental persistence. Regulations force producers to keep emissions in check, but that’s only one piece of the puzzle. I know researchers looking into safer alternatives or greener processes, such as water-based mixtures or silanes with lower toxicity. The push for sustainability drives many companies to recycle more or cut waste at every step, and vinylmethyldimethoxysilane chemists now pay closer attention to lifecycle impacts. Those efforts reflect a genuine move toward balancing industrial progress with everyday safety and environmental stewardship.
As industries evolve, they don’t let go of what works. Vinylmethyldimethoxysilane ties together many sectors—cables, buildings, electronics, and more. Connected by this invisible chemical link, countless modern products prove that small molecules can punch well above their weight. The future will likely bring even more efficient uses and eco-friendly approaches, built on decades of reliability and chemistry that continues to prove its worth.
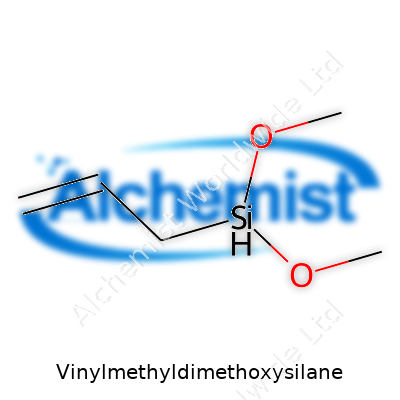
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | ethenyl(methoxy)dimethylsilane |
| Other names |
Trimethoxy(methyl)silane Dimethoxy(methyl)vinylsilane Vinylmethylbis(methoxy)silane Vinyldimethoxymethylsilane Methyldimethoxyvinylsilane |
| Pronunciation | /vaɪˌnɪlˌmɛθɪlˌdaɪˌmɛθɒksiˈsaɪleɪn/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 2768-02-7 |
| Beilstein Reference | 3191986 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:34249 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1545689 |
| ChemSpider | 87501 |
| DrugBank | DB13840 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03a234b6-e3a6-4bb6-a67a-79306d8c9b82 |
| EC Number | 220-940-2 |
| Gmelin Reference | 1261054 |
| KEGG | C18735 |
| MeSH | D014738 |
| PubChem CID | 12622 |
| RTECS number | GV7875000 |
| UNII | 1U3L6QF90L |
| UN number | UN2662 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID8020403 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H12O2Si |
| Molar mass | 148.24 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless transparent liquid |
| Odor | Sweet |
| Density | 0.950 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Hydrolyses |
| log P | 1.6 |
| Vapor pressure | 1.7 hPa (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 14.8 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 12.6 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -7.52e-6 cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.3900 |
| Viscosity | 0.38 mPa·s |
| Dipole moment | 3.14 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 233.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -307 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -3405 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | **"GHS02, GHS07, Danger, H226, H315, H319, P210, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313"** |
| Pictograms | Flame, Exclamation mark |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P362+P364, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0 |
| Flash point | 64 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 440 °C |
| Explosive limits | Explosive limits: 1.1% (LEL) – 8.9% (UEL) |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50/oral/rat = 7300 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral rat LD50 > 2000 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | GVG512 |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL: Not established |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Not Listed |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Vinyltrimethoxysilane Vinyltriethoxysilane Methyltriethoxysilane Dimethyldimethoxysilane Trimethylmethoxysilane |